|
 |
Compatibility of Thermoplastic Polyurethanes
with Drugs for IV Sets
Ms. Elena Draganoiu, Global Technology Manager,
Lubrizol LifeSiences, USA.
Yolanda Zhu1, Clark Yan1, Wei-bo Qiu1, Hong Zhang2, Elena Draganoiu3
1Lubrizol LifeSciences, Lubrizol Specialty Chemicals Co., Ltd., Shanghai,
China,
2Institute of Chemistry Research, China National Science Academy, Beijing,
China,
3Lubrizol LifeSciences, Lubrizol Advanced Materials, Inc., Cleveland, OH,
USA |
Introduction
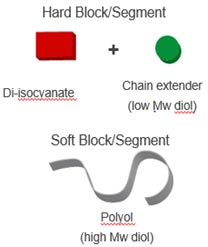
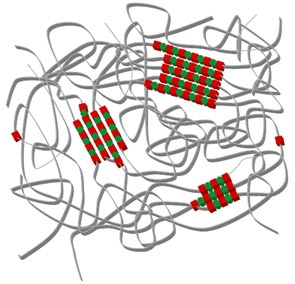
Thermoplastic polyurethanes(TPU) are formed by step-growth polymerization
between di-isocyanates and diols. Polymeric diol and isocyanate groups aggregate
to form a two phase domain structure consisting of :
- Soft segments (low Tg) - contribute to the elasticity / flexibility
- Hard segments (urethane) form crystalline domains and physical crosslinks due
to hydrogen bonding; they confers mechanical strength
TPU schematic structure
 |
 |
TPUs have a long history of proven biocompatibility and
in vivo stability in biomedical applications, including cardiovascular
(central venous catheters, heart pacemaker connectors, cardiac assist pump
bladders, tubing, housing, coatings, lead insulators, vascular grafts,
patches, percutaneous shunts), urology (catheters, hemodialysis tubing,
membranes), orthopedics (orthopedic splints, bone adhesives), wound care,
etc.
Pellethane® TPUs produced by Lubrizol LifeSciencesare
aromatic polyether and polyester TPUs available in natural color and in a
wide range of durometers. Specially developed extrusion and molding grades
allow ease of use with existing equipment and minimal modifications.
Pellethane® TPUs are widely used for a variety of medical applications
including tubing, catheters and implants due to their attributes: |
• Excellent biostability and biocompatibility
• Outstanding hydrolysis resistance and non-hemolytic properties
• Plasticizer free
• Good compression strength, excellent kink resistance, flexibility and softness
• Superior clarity
• Greater strength with good flexibility compared to PVC, allowing thinner wall
tubes ab fluid storage bags with enhanced burst resistance
• Easily incinerated, no corrosive or dangerous chemical emissions
• Manufactured on world class ISO 9001:2008 facilities
The use of thermoplastic polyurethanes for intravascular (IV) sets has seen a
recent increase, however comprehensive testing to evaluate their compatibility
with drugs has not been conducted prior to this study.
Compatibility between medications and intravascular administration sets
(containers, tubing, and delivery) is important for administration of prescribed
medications to assure predictable delivery of the drug dose, safety and
efficacy. Potential interactions between drugs and IV sets include:
Sorption
• Adsorption of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) to the inner
surface (without further penetration) results in initial reduction in drug
concentration delivered to the patient and as the surface become saturated,
concentration restores
• Absorption of the API into the material. The drug concentration in the
infusate is initially low and slowly recovers as the material becomes saturated
• Permeation - drug migrates through the material and out onto the outer
surface of the IV set. Substantial drug loss that continues throughout the
duration of administration
• Leaching - components of IV sets (plastics) migrate to drug
• Polymer modification - drug modifies properties of the IV set (polymer)
The purpose of this study was to evaluate in vitro compatibility of IV sets
of thermoplastic polyurethanes with an array of drugs with different properties.
Methodology
Three types of infusions sets (manufactured by Jiangsu Suyun Medical Materials
Co., Ltd., China) were tested :
• Thermoplastic polyurethane set made from Pellethane® TPU
• Styrene butadiene thermoplastic elastomer set (TPE)
• Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) set (standard PVC with diethylhexyl phthalate)
All sets had similar tube design: OD 4 mm,ID 2.4mm, length 1.6m (Fig. 1-3).
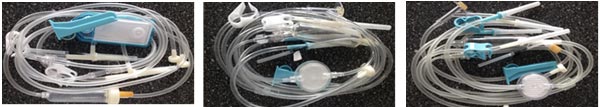
Fig. 1. TPU IV set Fig.
2. TPE IV set Fig.
3. PVC IV set
The study included seven common IV drugs, to cover different properties (aqueous
solubility and log P) and therapeutic classes as shown in also tested. The study
parameters (drug dose, volume, concentration, flow rate, administration time)
were designed to simulate clinical administration (Table 1).
The concentration of drug in the solution circulated through the IV sets was
quantified at different time intervals by high performance liquid chromatography
with UV detection, using reference standards. The impurity level, pH of the
solution and particulates were measured before and after circulation in the IV
sets. IV sets based on TPE and PVC were also evaluated for comparison. |

